Leetcode Solution - Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Problem Statement You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of…
October 05, 2020
You are given a rows x cols matrix grid. Initially, you are located at the top-left corner (0, 0), and in each step, you can only move right or down in the matrix.
Among all possible paths starting from the top-left corner (0, 0) and ending in the bottom-right corner (rows - 1, cols - 1), find the path with the maximum non-negative product. The product of a path is the product of all integers in the grid cells visited along the path.
Return the maximum non-negative product modulo 109 + 7. If the maximum product is negative return -1.
Notice that the modulo is performed after getting the maximum product.
Example
Input: grid = [[-1,-2,-3],
[-2,-3,-3],
[-3,-3,-2]]
Output: -1 (Not found any non-negative product)
Input: grid = [[1,-2,1],
[1,-2,1],
[3,-4,1]]
Output: 8 (1 * 1 * -2 * -4 * 1 = 8)
Input: grid = [[1, 3],
[0,-4]]
Output: 0 (1 * 0 * -4 = 0).
Input: grid = [[ 1, 4,4,0],
[-2, 0,0,1],
[ 1,-1,1,1]]
Output: 2 (1 * -2 * 1 * -1 * 1 * 1 = 2).Please note the restrictions:
10^9 + 7In every solution, we will traverse like below:
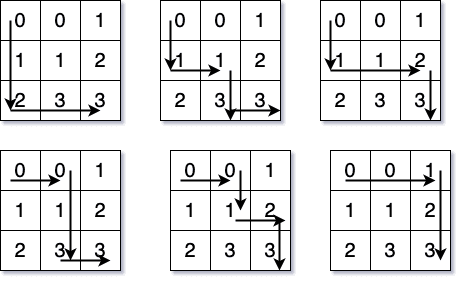
Lets look at the algorithm:
private long prod = -1;
private int modulo = (int)Math.pow(10, 9) + 7;
private long getProd(List<Integer> list) {
long p = 1;
for (Integer item : list) {
p *= item;
}
return p;
}
private void find(int[][] grid, int x, int y, List<Integer> list) {
if (x < grid.length && y < grid[0].length) {
list.add(grid[x][y]);
}
if (x == grid.length-1 && y == grid[0].length-1) {
//find product
this.prod = Math.max(this.prod, this.getProd(list));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return;
}
else if (x >= grid.length || y >= grid[0].length) {
return;
}
find(grid, x+1, y, list);
find(grid, x, y+1, list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
public int maxProductPath(int[][] grid) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
this.find(grid, 0, 0, list);
return (int)this.prod % this.modulo;
}You can re-write above find() as below:
private void find(int[][] grid, int x, int y, List<Integer> list) {
list.add(grid[x][y]);
if (x == grid.length-1 && y == grid[0].length-1) {
//find product
this.prod = Math.max(this.prod, this.getProd(list));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return;
}
if (x+1 < grid.length) {
find(grid, x+1, y, list);
}
if (y+1 < grid[0].length) {
find(grid, x, y+1, list);
}
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}Its O(n^3), as for every cell, you are traversing the whole matrix (almost)
Basically, where we need to calculate the product of the list, we can pass the product as parameter to the function. And, we don’t need to keep the list now.
See
private long prod = -1;
private int modulo = (int)Math.pow(10, 9) + 7;
private void find(int[][] grid, int x, int y, long product) {
if (x >= grid.length || y >= grid[0].length) {
return;
}
if (x == grid.length-1 && y == grid[0].length-1) {
this.prod = Math.max(this.prod, product * grid[x][y]);
return;
}
find(grid, x+1, y, product * grid[x][y]);
find(grid, x, y+1, product * grid[x][y]);
}
public int maxProductPath(int[][] grid) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
long product = 1;
this.find(grid, 0, 0, product);
return (int)this.prod % this.modulo;
}Its same as above O(n^3)
If you see closely, we are repeating our calculations again and again for some cells. We can save those results in a temporary cache. This solution is called DP (Dynamic Programming).
private long prod = -1;
private int modulo = (int)Math.pow(10, 9) + 7;
private long getProd(List<Integer> list) {
long p = 1;
for (Integer item : list) {
p *= item;
}
return p;
}
private void find_dp(int[][] grid, int x, int y, List<Integer> list, int[][] dp) {
if (dp[x][y] != 0) {
this.prod = Math.max(this.prod, dp[x][y]);
return;
}
if (x < grid.length && y < grid[0].length) {
list.add(grid[x][y]);
}
if (x == grid.length-1 && y == grid[0].length-1) {
//find product
this.prod = Math.max(this.prod, this.getProd(list));
dp[x][y] = (int)this.prod;
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return;
}
else if (x >= grid.length || y >= grid[0].length) {
return;
}
find(grid, x+1, y, list);
find(grid, x, y+1, list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
public int maxProductPath(int[][] grid) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int[][] dp = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];
this.find_dp(grid, 0, 0, list, dp);
return (int)this.prod % this.modulo;
}Its O(n^2)
Problem Statement You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of…
Problem Statement You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate…
Problem Statement Write a function to find the longest common prefix string…
Problem Statement Given a string, find the length of the longest substring…
Its a tree based data structure which is a complete binary tree(all nodes have…
It is one of a simple algorithm to study for a beginner to understanding sorting…
Introduction In this post we will see following: How to schedule a job on cron…
Introduction There are some cases, where I need another git repository while…
Introduction In this post, we will see how to fetch multiple credentials and…
Introduction I have an automation script, that I want to run on different…
Introduction I had to write a CICD system for one of our project. I had to…
Introduction Java log4j has many ways to initialize and append the desired…